Written by Professor Rebecca L. Cooney
In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, immersive learning has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how knowledge is acquired and retained. Artificial intelligence (AI), simulations, and experiential learning can be transformative for students and harnessed to create engaging educational opportunities.
So, what are some real-world applications in education? How can you design powerful, immersive learning content while overcoming challenges and embracing the future?
According to Elon University’s Center for Engaged Learning, six primary characteristics of practices fall under the umbrella term of immersive learning.
1. Time and focus refer to the length of time a learner is given for an individual learning task or the time-bound frequency and spacing of learning activities. Immersive learning experiences can be short and in real-time or implemented asynchronously over a period of time.
2. Authenticity refers to the level of direct and tangible engagement a student has with the learning experience. The goal is to design activities that are realistic, relatable, and relevant.
3. The most effective immersive learning opportunities challenge students to be independent thinkers who take ownership of the experience. They play an active role in learning versus passive participants.
4. Learning can be a disruptive process and affect our worldview. Immersive learning experiences such as internships, simulations, or community-based learning have an increased potential for students to experience distortion or conflict if it falls outside their norms.
5. Reflection is a great way to connect immersive experiences to other learning and to the world beyond the classroom. Tools and techniques around reflection are an invaluable component of an immersive learning experience.
6. Guidance and facilitation around immersive experiences — no matter how simple or complex — is critical. Students will get more out of it if they have clear directions and expectations. The best role a facilitator can take is “guide on the side” and as a co-learner.
In summary, Elon University states that “Immersive learning refers to a multifaceted approach to teaching and learning that encompasses various methodologies and is not restricted to a particular subject or profession. It involves creating educational experiences where certain essential conditions are present, which can include hands-on experiences, in-person interactions, experiential learning, and real-world applications across diverse contexts.”
Immersive learning is grounded with a solid scientific foundation. Its practical applications in education offer tangible benefits, while strategies for designing experiential learning content present endless opportunities.
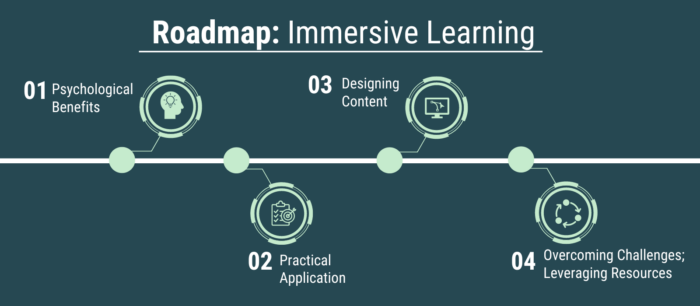
Despite challenges, this immersive learning roadmap reveals four key stops: exploring psychological benefits, understanding practical applications, mastering content design, and overcoming challenges while leveraging available resources.
1. Psychological Benefits
Immersive learning engages multiple senses to stimulate a deeper comprehension and longer-lasting retention of knowledge. Emotions are pivotal in this process, combined with attention, problem-solving, and memory — all crucial facets of learning. Familiar statistics …
We remember:
- 10% of what we read
- 20% of what we hear
- 30% of what we see
- 70% of what we discuss with others
- 80% of what we personally experience
So it is no surprise that students learn by doing. Within the structured confines of immersive experiences, students feel secure, allowing them to fully immerse themselves in learning. These scenarios often mimic real-life situations and empower learners to apply their knowledge practically — a useful skill in the workplace. Therefore, by engaging students in interactive activities, educators provide them with invaluable examples and stories to share in interviews and networking circles.
2. Practical Application: Types of Practice
Community-based learning fosters meaningful interactions by involving students in service-oriented projects and community engagement initiatives. For example, students might collaborate with a local nonprofit organization to create a community garden or assist a nearby business in developing a marketing strategy.
Global education combines disciplinary knowledge with intercultural understanding. Study abroad programs are a prime example. In addition, hands-on activities both in and out of the classroom (e.g., fieldwork, observation, and virtual reality simulations) offer invaluable practical engagement opportunities. Work-integrated learning mirrors the professional world by immersing students in specific career pathways through internships and co-op programs. Interactive simulations (e.g., Stukent® Simternships™) are another example of activities that replicate professional settings through structured exercises like role-playing, real-time crisis response, or problem-solving challenges.
3. Designing Content
When crafting an immersive learning experience, it all begins with pinpointing your desired learning outcomes. What do you envision your students gaining from this experience? With a plethora of options such as AR, VR, AI, and simulations, how does one decide where to dive in?
As educators, we often find ourselves navigating this terrain solo, managing our classrooms with limited resources and budgets. So, selecting the right technology hinges on what aligns best with your students, the subject matter, and the tools at your disposal. This means it is crucial to consider factors like logistics, cost, and even your own comfort level. For example, while a university may offer VR headset rentals, the logistics and cost may not always be feasible for the entire class.
Mere experimentation with technology may not suffice, so it is imperative to tailor specific activities to its usage. Think about role-playing exercises, interactive simulation rounds, or problem-solving tasks coupled with assessments or reflections. Adding interactive elements such as quizzes and polls can further bolster engagement and understanding among learners.
Feedback is also paramount in this journey. Techniques like peer reviews foster motivation and enhance student engagement. Continually evaluating the effectiveness of your immersive learning program through data collection ensures ongoing improvement for both you and your students. The best advice … be brave! Venturing into the realm of immersive technology and experiential learning may seem daunting, but the rewards are worth it in the end.
4. Overcoming Challenges and Leveraging Resources
Learning is enhanced through immersive experiences, but it is important to acknowledge inherent challenges. Technological barriers such as limited headsets and unstable internet connectivity can hinder progress, as can the potential for overstimulation, particularly among students with ADHD or anxiety. While immersive techniques offer unique learning opportunities, they may lack the depth and feedback of traditional methods. This is compounded by the possible significant cost of scaling immersive activities.
Educators can implement various strategies to address these challenges and cultivate a more inclusive learning environment. Offering technical support and alternative platforms aids in navigating technology barriers, while customizing experiences caters to diverse learning preferences. Incorporating collaborative activities and ensuring instructor engagement enhance learning outcomes and depth of understanding.
Cost considerations can be managed through sharing resources, using free tools, and strategically implementing immersive experiences. Ensuring inclusivity involves applying universal design principles and accommodating students with specific needs. Balancing immersive learning with traditional methods and maintaining variety in activities sustains engagement while addressing limitations.
Continuous improvement is crucial in the immersive learning journey as well. Establishing feedback loops allows educators to refine activities based on student insights, while adaptability to evolving technology ensures optimization.
By adopting these strategies, educators can navigate the challenges of immersive learning and create a more inclusive, engaging, and effective learning environment for their students.
Resources
- Capsule Sight (2023). 15 Examples of the Use of Mixed Reality in Education
- ClassVR (2022). 5 Best Virtual Reality in Education Examples
- Digital Learning Institute. Immersive Learning and the Metaverse
- eLearning Industry (2022). Immersive Learning Design Today: Best Practices
- Elon University Center for Engaged Learning. Immersive Learning
- Forbes (2021). 10 Best Examples of VR and AR in Education
- KnowledgeHut (2024). Immersive Learning: Implementation, Best Practices, Benefits
- Stukent Simternships: Overview and List of Simternships
Rebecca L. Cooney is a Les Smith Distinguished Professor of Communication at Washington State University. She teaches courses in branding, advertising, and digital marketing, leads undergraduate assessment efforts for Murrow College, and serves as a co-investigator on a grant focused on interactions between natural products and prescription drugs. She leads assessment efforts for her college, is professionally certified in learning experience design, and holds a BA and MA in communication.






